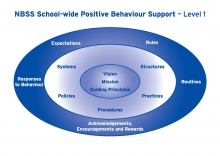
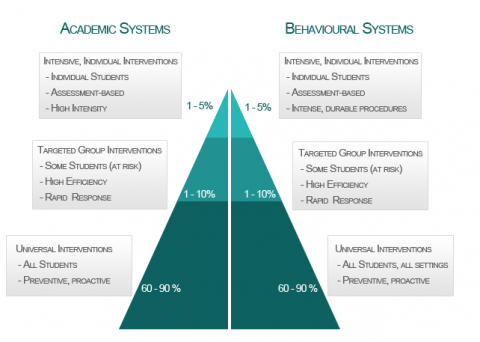
The National Behaviour Support Service offers three levels of support to partner second level schools:
- Level 1: School-wide Support for All Student
- Level 2: Targeted Intervention Support for Some Students
- Level 3: Intensive Individualised Support for a Few Students
The NBSS model of support draws extensively from Positive Behavioural Interventions and Supports (Sugai & Horner, 2002), Response to Intervention (Fuchs & Fuchs, 2006) and the Comprehensive, Integrated, Three-Tiered Model of Prevention (Lane, Kalberg, & Menzies, 2009) frameworks. The integration of these frameworks offers opportunities to address the behavioural needs as well as the social, emotional and academic needs of students effectively, with interventions at different levels of intensity and support. This problem-solving model is founded on international best practice (Bonhanon et al., 2006; Carr et al., 2002; Duffy & Scala, 2012; Ehren, Deshler, & Graner, 2010; Hawken & Horner, 2002; Lewis & Sugai, 1999; McPeak, Trygg, Minadaki, & Diana, 2007).
'CI3T models are data-informed, graduated systems of support constructed to address academic, behavioural, and social domains, with an overarching goal of supporting all learners in inclusive environments by maximizing available expertise through professional collaborations among school personnel' (Lane, Kalberg, & Menzies, 2009).
'RtI…integrates assessment and intervention within a multi-level prevention system to maximize student achievement and to reduce behavioral problems. With RtI, schools use data to identify students at risk for poor learning outcomes, monitor student progress, provide evidence-based interventions and adjust the intensity and nature of those interventions depending on a student’s responsiveness, and identify students with learning disabilities or other disabilities' (National Centre on Response to Intervention 2010, p 4).
'PBIS is a proactive systems approach to establishing the behavioral supports and social culture and needed for all students in a school to achieve social, emotional, and academic success.' (www.pbis.org)
In NBSS partner schools this three-tiered approach is applied to behaviour interventions as well as interventions that address the social, emotional and academic literacy and learning needs of students. All three levels of support to NBSS partner schools are customised to the specific characteristics, needs and requirements of each partner school on an on-going basis as change occurs. NBSS interventions and support emphasis using evidence-based practices for promoting behaviour change.
All work undertaken aims to promote positive behaviour and learning throughout the school by focusing on developing:
- Behaviour for Learning Skills
- Social and Emotional Literacy Skills
- Academic Literacy and Learning Skills
- Wellbeing Skills.
Find out more about our work by clicking on the link below
- The NBSS in Schools gives a brief overview of the work of the National Behaviour Support Service in partner schools and presents many of the interventions, projects and initiatives schools implement in the areas of (a) Behaviour for Learning skills development (b) Social & Emotional Literacy skills development (c) Academic Literacy and Learning skills development and (d) Wellbeing skills development.